FFT解决大数乘法
前言
FFT是至今让我感觉最绝望的东西,因为真的除了模板题勉强能做,剩下的完全就做不了了QAQ
FFT用于加速多项式乘法计算,从O(n^2)优化到O(nlogn),在其他领域用的很广,在ACM领域可以用来算大数乘法,更重要的是用来计算卷积,加速DP,这类题目神难……
还有就是FFT本身难,下面的代码没有理论基础的话,十有八九是看不懂的,除了数学大佬和高智商大佬orz,而且有了理论基础,模板也不一定看得懂……会了模板,题目还是不会做…………
个人感觉FFT需要的理论基础有:线性代数,欧拉方程,复数的运算
- FFT详解
https://blog.csdn.net/ggn_2015/article/details/68922404
https://www.zybuluo.com/397915842/note/37965 - 二进制反转
https://blog.csdn.net/GGN_2015/article/details/69518685
大数乘法 V2 问题 - 51Nod-1028
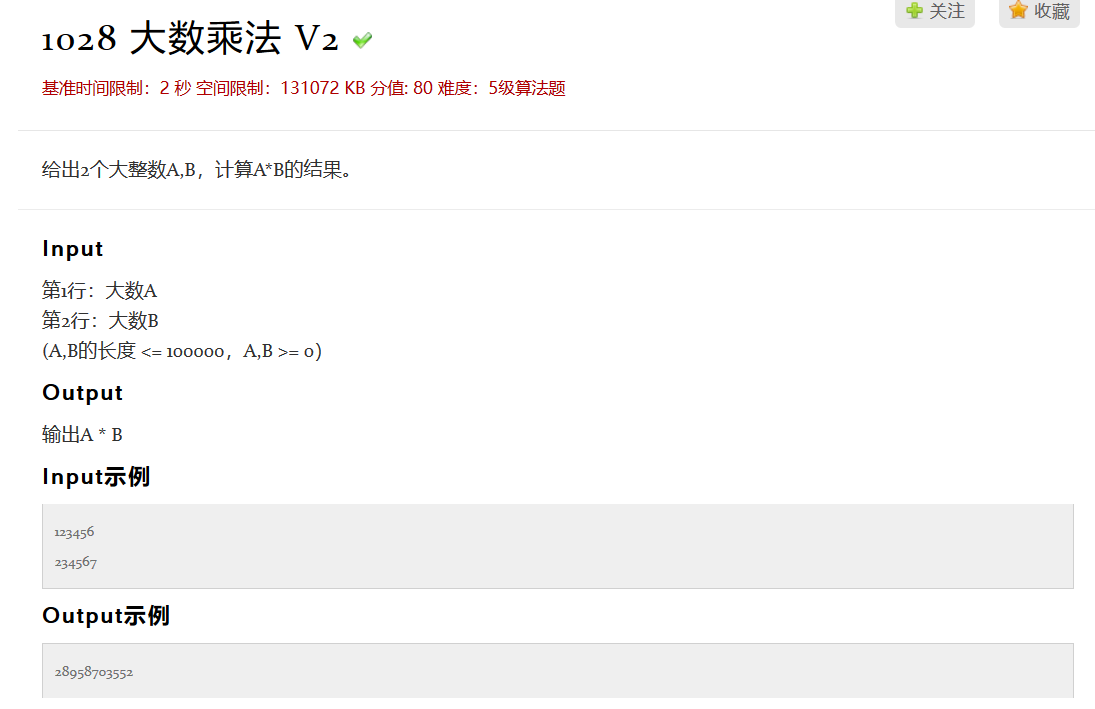 题目大意
题目大意
模板题
思路
使用std的complex类做,旋转因子用 wn = exp(PI*i/(n/2))
这是第一道我能把注释写得如此详细的题目……
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <complex>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int N = 3e5 + 15;
const double PI = acos(-1);
typedef complex<double> cd;
cd a[N], b[N]; //complex数组
int rev[N]; //记录反转二进制数字
char s1[N], s2[N];
int ans[N];
//getRev:
//作用:生成1 到 2^bit(也就是s)的颠倒二进制数的数组
//原理:将当前数字二进制反转,即是
//当前数字前bit - 1位的颠倒结果右移一位 + 当前数字末位移到最高位
//其中前者的工作已经在rev[i >> 1]生成的时候完成了,所以把这个值直接右移一位,
//再加上当前数字末位最高位
void getRev(int bit){ //bit = log2(s)
for(int i = 0; i < (1 << bit); i++){
rev[i] = ((rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | ((i&1) << (bit - 1)));
}
}
//fft:
//作用:计算dft(系数式转点值式)和idft(点值式转系数式)
//参数:
// cd a[]: 系数表达式中的系数向量
// int n: 结果的点值表达式的次数界
// int dft:传1进行dft,传-1进行idft
void fft(cd a[], int n, int dft){
//根据得到的rev数组调整a,为下一步的循环做准备
//加入 if(i < rev[i]),防止双次交换变回原样
//建议debug看一下原理
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(i < rev[i]) swap(a[i], a[rev[i]]);
}
//step为每次的步长,从底层递推回去,因此
//不需要走到n,只需要走到step/2
for(int step = 1; step < n; step <<= 1){
//计算单位复根,根据消去引理,计算的是w[n/2](k),而不是w[n](2k)
cd wn = exp(cd(0, PI*dft/step));
//计算每一个块,具体可看《算法导论》的那颗树
//加上step << 1是因为下面是同时跑k和k+step的,总共就跑了step << 1
for(int j = 0; j < n; j += step << 1){
//递归时同深度的子树相互独立,因此递推回去也是一样
cd wnk(1, 0);
for(int k = j; k < j + step; k++){
cd x = a[k];
cd y = wnk*a[k + step];
a[k] = x + y;
a[k + step] = x - y;
wnk*=wn;
}
}
}
if(dft == -1){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) a[i] /= n;
}
}
int main(){
while(~scanf("%s%s", s1, s2)){
memset(ans, 0, sizeof(ans));
int len_s1 = strlen(s1), len_s2 = strlen(s2);
for(int i = 0; i < len_s1; i++) a[i] = cd(s1[len_s1 - i - 1] - '0', 0);
for(int i = 0; i < len_s2; i++) b[i] = cd(s2[len_s2 - i - 1] - '0', 0);
//找到第一个超过(len_s1 + len_s2 - 1)的2的整数幂s作为次数界,并记录下指数bit
//bit给getRev函数用, s给fft函数用
int bit = 1, s = 2;
for(bit = 1; s < len_s1 + len_s2 - 1; bit++, s <<= 1);
//调用getRev函数生成反转二进制,从1到2^bit - 1
getRev(bit);
//将a和b转为点值式,并相乘
//将相乘的结果
fft(a, s, 1);
fft(b, s, 1);
for(int i = 0; i < s; i++) a[i] * = b[i];
fft(a, s, -1);
//还原成十进制,目前表达式是
//a[0] + a[1] * x + a[2] * x^2 + ... + a[s - 1] * x^(s - 1)
//其中a[i]并不一定是10以内的数,所以该进位的要进位
for(int i = 0; i < s; i++){
ans[i] += (int)(a[i].real() + 0.5);
ans[i + 1] += ans[i]/10;
ans[i] %= 10;
}
//输出答案,去掉前导0
int* p = ans + len_s1 + len_s2;
while(* p == 0 && p != ans - 1) p--;
if(p == ans - 1){
printf("0\n");
}else{
while(p != ans - 1){
printf("%d", * p);
p--;
}
puts("");
}
}
return 0;
}
Bull Math - POJ 2389
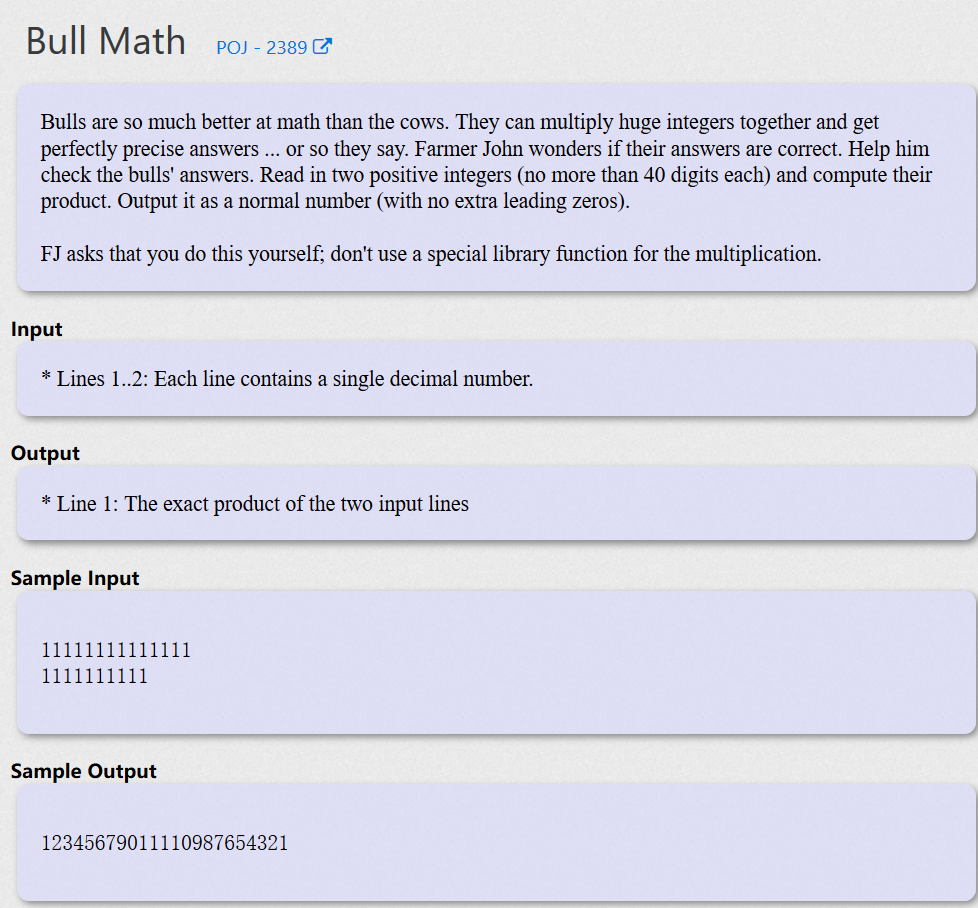 题目大意
题目大意
同样是大数乘法
思路
本题可模拟做,当然这里用FFT做
复数类是自己写的,wn取 i*sin(PI/(n/2)) + cos(PI/(n/2))
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 200;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
struct cd{
double real, imag;
cd(double _real = 0, double _imag = 0): real(_real), imag(_imag) {}
cd operator + (cd _obj) { return cd(real + _obj.real, imag + _obj.imag);}
cd operator - (cd _obj) { return cd(real - _obj.real, imag - _obj.imag);}
cd operator * (cd _obj) { return cd(real * _obj.real - imag * _obj.imag, real * _obj.imag + imag * _obj.real);}
cd operator * (double _real) { return ( * this) * cd(_real, 0);}
cd operator = (double x) { real = x, imag = 0; return *this;}
};
cd a[N], b[N];
int rev[N];
char s1[N], s2[N];
int ans[N];
inline void init(){
memset(a, 0, sizeof(a));
memset(b, 0, sizeof(b));
memset(ans, 0, sizeof(ans));
}
inline void getRev(int bit){
for(int i = 0; i < (1 << bit); i++){
rev[i] = ((rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i&1) << (bit - 1));
}
}
void mswap(cd& x, cd& y){
cd temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
void fft(cd a[], int n, int dft){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(i < rev[i]) mswap(a[i], a[rev[i]]);
}
for(int step = 1; step < n; step <<= 1){
cd wn(cos(dft*PI/step), sin(dft*PI/step));
for(int j = 0; j < n; j += step << 1){
cd wnk(1, 0);
for(int k = j; k < j + step; k++){
cd x = a[k];
cd y = wnk*a[k + step];
a[k] = x + y;
a[k + step] = x - y;
wnk = wnk*wn;
}
}
}
if(dft == -1){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
a[i].real /= n;
}
}
}
int main(){
while(~scanf("%s%s", s1, s2)){
init();
int len_s1 = strlen(s1), len_s2 = strlen(s2);
for(int i = 0; i < len_s1; i++)
a[i] = (s1[len_s1 - i - 1] - '0');
for(int i = 0; i < len_s2; i++)
b[i] = (s2[len_s2 - i - 1] - '0');
int bit = 1, s = 2;
for(bit = 1; s < len_s1 + len_s2 - 1; bit++, s <<= 1);
getRev(bit);
fft(a, s, 1);
fft(b, s, 1);
for(int i = 0; i < s; i++) a[i] = a[i]*b[i];
fft(a, s, -1);
for(int i = 0; i < s; i++){
ans[i] += (int)(a[i].real + 0.5);
ans[i + 1] += ans[i]/10;
ans[i] %= 10;
}
int* p = ans + s;
while(p != ans - 1 && *p == 0) p--;
if(p == ans - 1){
printf("0\n");
}else{
while(p != ans - 1){
printf("%d", *p);
p--;
}
puts("");
}
}
return 0;
}


