纯优先队列题目、用优先队列解决带权值的BFS问题、用优先队列优化Dijkstra算法
前言
周六的华工的比赛自己打得和鬼一样……还是那句话,“ACM之路任重道远”,嗯,好好学习!
回到正题,最近看Lewin大佬一直在发优先队列,想到自己还没过这个点,就顺便刷了一下,本来想再多刷点再发,但是貌似没什么时间了就先这样吧
目前看来,优先队列作为一种数据结构可以用来解决带权值的BFS问题,还可以用来优化Dijkstra算法,另外也可以用来优化Prim最小生成树算法,不过那个我至今都还没啃所以等以后啃了直接发优化版本,当然还有纯用优先队列解决的题目
在C++中,优先队列是不用自己写的,STL中有priority_queue,直接拿来用就可以了,所以重点在于如何建立模型使用优先队列(JAVA自己不会所以不提)
Stones - HDU 1896
 题目大意
题目大意
小明走路去上学,路上有n个石头,第i个石头的位置是xi,能抛出去的最远距离是di,现在小明very无聊,他走在路上遇到第奇数块石头就把它往前抛出去,遇到第偶数块就不理它,另外小明更喜欢大块的石头(di更小的),如果不同石头落在相同位置他会先选择那块大的,现在问到最后最远的石头离小明的出发点有多远
思路
优先队列的水题,石头全部入队列,每次出队列xi最小的且di最小的,是第奇数块就入队列(xi + di, di),偶数块不理,开个变量ans维护距离最大值直到队列为空就可以了
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
struct stone{
int p, d;
stone(int pp = 0, int pd = 0): p(pp), d(pd) {}
bool operator <(const stone& b) const{
if(p != b.p) return p > b.p;
else return d > b.d;
}
};
priority_queue<stone> que;
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--){
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
while(n--){
int p, d;
scanf("%d%d", &p, &d);
que.push(stone(p, d));
}
int i = 1;
int ans = 0;
while(!que.empty()){
stone u = que.top();
que.pop();
ans = max(ans, u.p);
if(i){
stone v(u.p + u.d, u.d);
que.push(v);
}
i ^= 1; //维护奇偶
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}
确定比赛名次 - HDU 1285
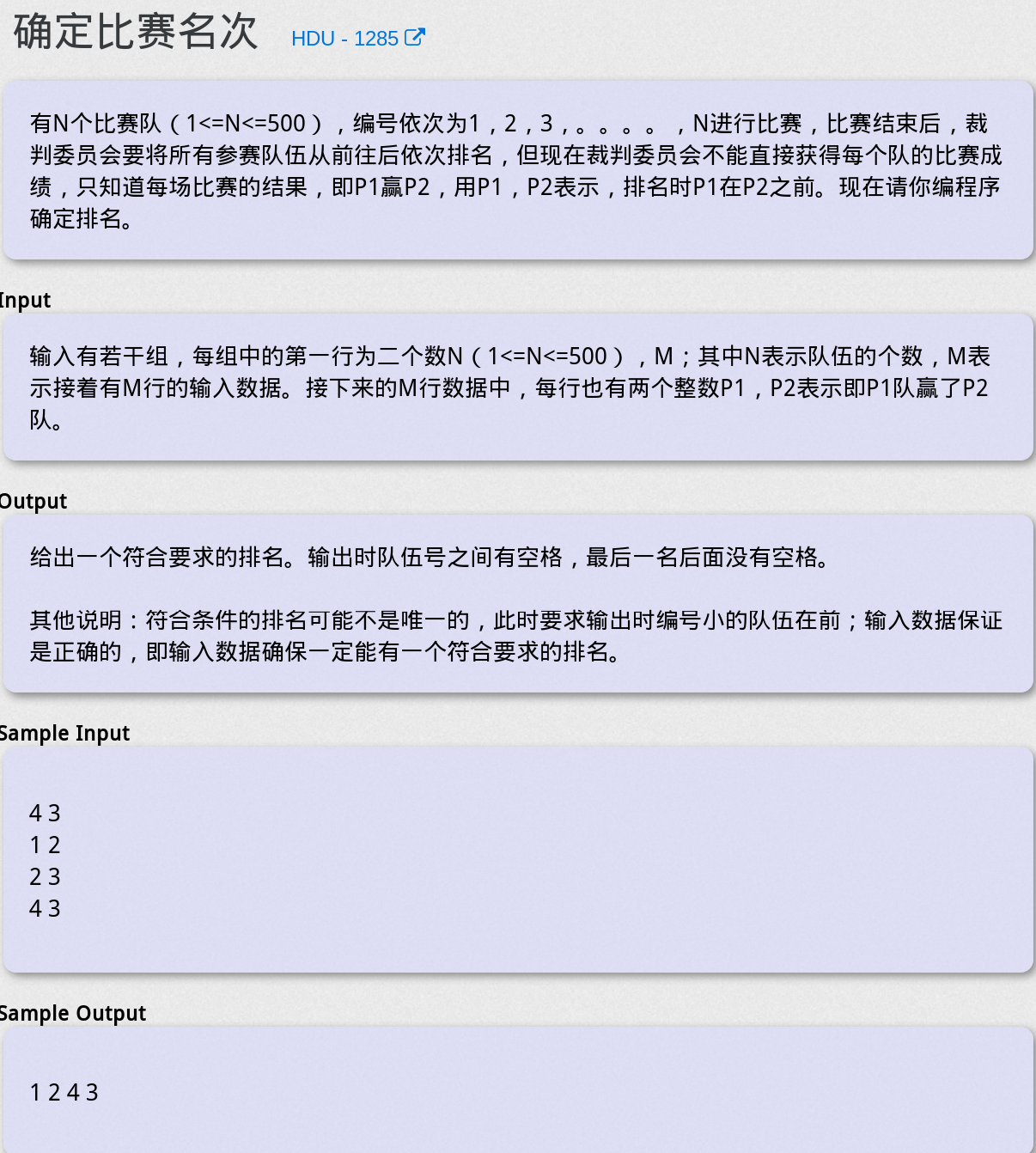 题目大意
题目大意
(假装有解释)
思路
仍然是水题,只是没有上面那道题那么水
这是拓扑排序的典型题目了,不过因为要输出编号小的,所以原来的队列要维护编号最小值
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <functional>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e5 + 15;
struct edge{ int to, next;};
edge e[N];
int head[N];
int tot;
int idg[N];
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > que;
inline void init(){
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
memset(idg, 0, sizeof(idg));
tot = 0;
}
inline void addEdge(int u, int v){
e[tot].to = v;
e[tot].next = head[u];
head[u] = tot++;
idg[v]++;
}
void topoSort(int n){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(!idg[i]) que.push(i);
}
while(!que.empty()){
int u = que.top();
que.pop();
for(int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].next){
int v = e[i].to;
idg[v]--;
if(!idg[v]) que.push(v);
}
printf((!que.empty()) ? "%d " : "%d\n", u);
}
}
int main(){
int n, m;
while(~scanf("%d%d", &n, &m)){
init();
while(m--){
int u, v;
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
addEdge(u, v);
}
topoSort(n);
}
}
New Year Snowmen - CodeForces-140C
 题目大意
题目大意
在一个数组中任意取三个互不相同的数,重复这个过程并且规定取了的数不能再取,问怎么取能使得取的次数最多?
思路
从直觉来看,当然是 优先取数量最多的那个数(可能是生活经验吧)
所以开个map记录每个数的出现次数,然后把(数, 数出现的次数)入队列,优先取出现次数最多的三个数出队列,作为一次取的操作,存入答案数组并降序排序,然后将他们各自的次数自减,如果还是大于0就继续入队列,直到队列内的元素不到3个
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <functional>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 15;
struct node{
int val, cnt;
node(int pval = 0, int pcnt = 0): val(pval), cnt(pcnt) {}
bool operator < (const node& b) const {
return cnt < b.cnt;
}
};
map<int, int> mp;
priority_queue<node> que;
int ans[N][3];
int pos;
inline void init(){
mp.clear();
while(!que.empty()) que.pop();
pos = 0;
}
int main(){
int n;
while(~scanf("%d", &n)){
init();
while(n--){
int tmp;
scanf("%d", &tmp);
mp[tmp]++;
}
for(map<int, int>::iterator it = mp.begin(); it != mp.end(); it++){
que.push(node(it->first, it->second));
}
while(que.size() >= 3){
node nd[3];
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
nd[i] = que.top();
que.pop();
ans[pos][i] = nd[i].val;
nd[i].cnt--;
}
sort(ans[pos], ans[pos] + 3, greater<int>());
pos++;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
if(nd[i].cnt > 0) que.push(nd[i]);
}
}
printf("%d\n", pos);
for(int i = 0; i < pos; i++){
printf("%d %d %d\n", ans[i][0], ans[i][1], ans[i][2]);
}
}
}
Ignatius and the Princess I - HDU-1026
 题目大意
题目大意
王子救公主,每次从(0,0)走到(n - 1, m - 1),遇到怪兽就要打到他死才能走,每次走一步和攻击一次怪兽都耗费1s,每次攻击怪兽怪兽扣1点hp,现在给定图,求出王子完成该路径所需的最短时间。另外,规定开始点和结束点不会是墙,开始点没有怪兽,如果不能完成输出不能完成
思路
这题Lewin大佬发过题解,作为一道比较典型的带权值的BFS问题个人也写了一遍
用优先队列维护当前耗时最小的点, 最后如果某一时刻出队列的点正好是结束点,那么就可以return了,这就是答案了
另外本题要求打印路径,因为用优先队列维护的BFS是不连续的,所以前序点也要动态维护(因为这个WA了一次 :( )
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100;
const int dx[] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
const int dy[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
struct vertex{
int x, y, val, px, py;
vertex(int px = 0, int py = 0, int pval = 0): x(px), y(py), val(pval), px(-1), py(-1) {}
bool operator < (const vertex& b) const { return val > b.val; }
};
int G[N][N];
int prex[N][N], prey[N][N];
bool used[N][N];
priority_queue<vertex> que;
inline void init(int n, int m){
memset(used[0], false, sizeof(used));
prex[n - 1][m - 1] = -1, prey[n - 1][m - 1] = -1;
while(!que.empty()) que.pop();
}
int bfs(int n, int m){
que.push(vertex());
while(!que.empty()){
vertex u(que.top());
que.pop();
if(used[u.x][u.y]) continue;
used[u.x][u.y] = true;
prex[u.x][u.y] = u.px, prey[u.x][u.y] = u.py;
if(u.x == n - 1 && u.y == m - 1) return u.val;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
vertex v(u.x + dx[i], u.y + dy[i]);
if(v.x < 0 || v.x >= n || v.y < 0 || v.y >= m || G[v.x][v.y] == -1 || used[v.x][v.y]) continue;
v.val = G[v.x][v.y] + u.val + 1;
v.px = u.x, v.py = u.y;
que.push(v);
}
}
return 0;
}
inline void print(int x, int y, int& t){
if(!(~x)) return;
int px = prex[x][y], py = prey[x][y];
print(px, py, t);
if(~px){
printf("%ds:(%d,%d)->(%d,%d)\n", t++, px, py, x, y);
}
while(G[x][y]){
printf("%ds:FIGHT AT (%d,%d)\n", t++, x, y);
G[x][y]--;
}
}
int main()
{
int n, m;
while(~scanf("%d%d", &n, &m)){
init(n, m);
int ans;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
getchar();
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
char ch = getchar();
if(ch == '.') G[i][j] = 0;
if(ch == 'X') G[i][j] = -1;
if(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') G[i][j] = ch - '0';
}
}
ans = bfs(n, m);
if(!(~prex[n - 1][m - 1])){
printf("God please help our poor hero.\n");
}else{
int t = 1;
printf("It takes %d seconds to reach the target position, let me show you the way.\n", ans);
print(n - 1, m - 1, t);
}
printf("FINISH\n");
}
return 0;
}
最短路径问题 - HDU 3790
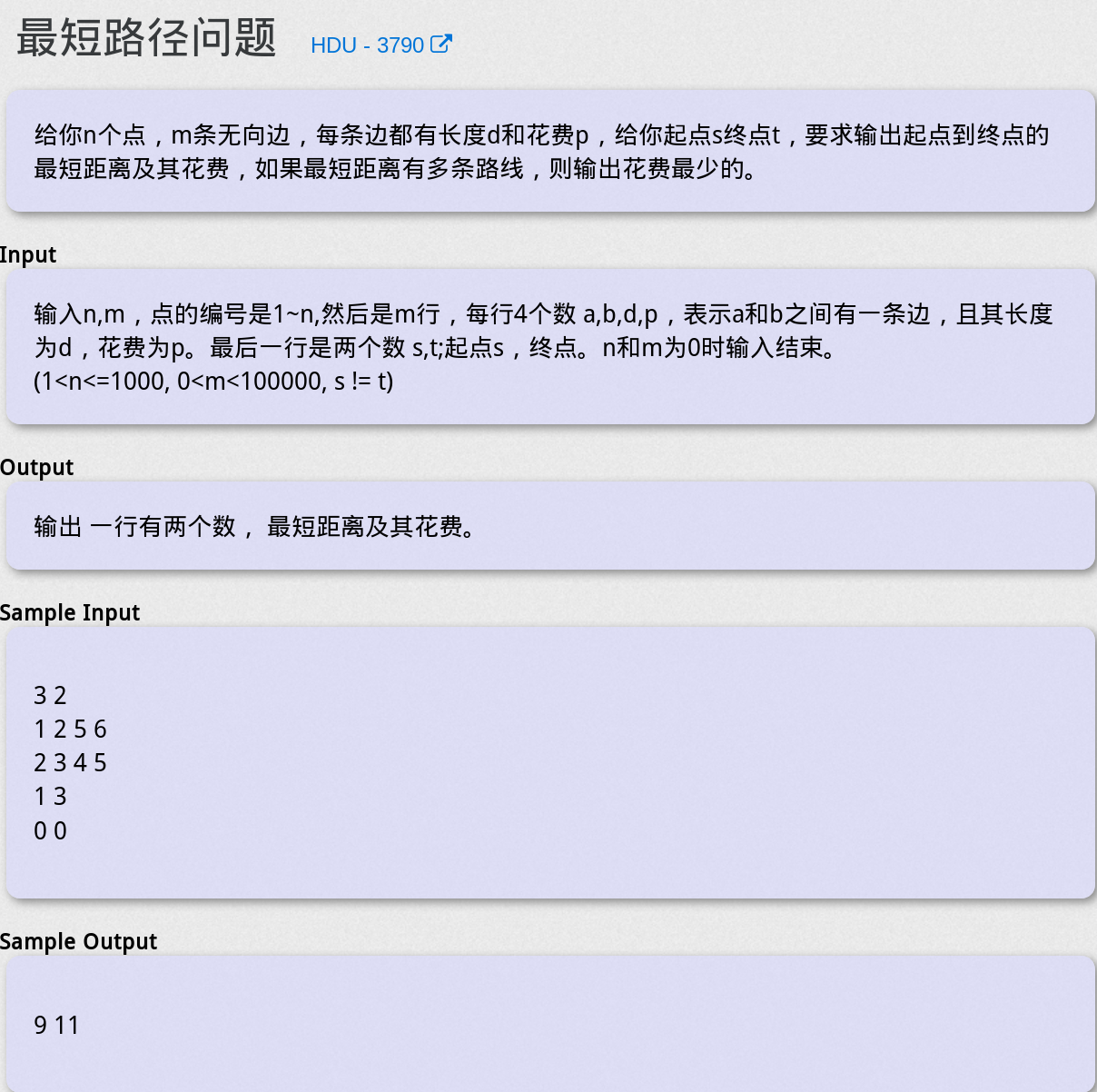 题目大意
题目大意
(假装有说明)
思路
冬训时Dijkstra的水题,这次用优先队列优化了一下Dijkstra算法
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000 + 15;
const int M = 100000 + 15;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
struct node{
int u, d, cost;
node(int pu, int pd = 0, int pcost = 0): u(pu), d(pd), cost(pcost) {}
bool operator < (const node& b) const{
if(d != b.d) return d > b.d;
else return cost > b.cost;
}
};
struct edge{ int to, next, d, cost; };
edge e[M];
int head[N];
int tot;
int cost[N], d[N];
priority_queue<node> que;
inline void init(){
while(!que.empty()) que.pop();
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
memset(cost, INF, sizeof(cost));
memset(d, INF, sizeof(d));
tot = 0;
}
inline void addEdge(int u, int v, int d, int cost){
e[tot].to = v;
e[tot].next = head[u];
e[tot].d = d;
e[tot].cost = cost;
head[u] = tot++;
}
inline node dijkstra(int s, int t){
que.push(node(s));
d[s] = cost[s] = 0;
while(!que.empty()){
node nd = que.top();
que.pop();
if(d[nd.u] < nd.d || (d[nd.u] == nd.d && cost[nd.u] < nd.cost)) continue;
if(nd.u == t) return nd;
for(int i = head[nd.u]; ~i; i = e[i].next){
int v = e[i].to;
if(d[v] > d[nd.u] + e[i].d || (d[v] == d[nd.u] + e[i].d && cost[v] > cost[nd.u] + e[i].cost)){
d[v] = d[nd.u] + e[i].d;
cost[v] = cost[nd.u] + e[i].cost;
que.push(node(v, d[v], cost[v]));
}
}
}
return node(s);
}
int main()
{
int n, m;
while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) && (n || m)){
init();
int s, t;
while(m--){
int u, v, ecost, ed;
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &u, &v, &ed, &ecost);
addEdge(u, v, ed, ecost);
addEdge(v, u, ed, ecost);
}
scanf("%d%d", &s, &t);
node ans = dijkstra(s, t);
printf("%d %d\n", ans.d, ans.cost);
}
return 0;
}


